
Indexing is everything – 5 reasons why your site isn’t showing up on Google
 Caroline Danielsson
Caroline Danielsson
Can’t find your website in Google’s search results? Then your customers can’t find it either! If your site isn’t showing up on Google Search, it may mean it hasn’t been indexed by the search engine — and in practice, that’s exactly what indexing means: the page being added to Google’s index. Unfortunately, there are several reasons why a site doesn’t appear in the search results. We’ve summarized the 5 most common reasons why a site isn’t being indexed and what you can do to check if you’re affected!
What does indexing mean?
So, what does indexing actually mean? Well, Google crawls websites on the internet and stores information about them. When someone performs a search, Google checks its index for the sites it believes are most relevant to that search. This storing of information means that the site is indexed by Google.
If your site isn’t indexed, it will never appear in Google’s search results. That’s because Google has no information about your site — it’s as if it doesn’t exist.
So, how do you know if your site is indexed? First, you need to figure out whether it is indexed or not. An easy way is to type the following into Google’s search bar:
site:https://www.yourdomain.com
Do you only see the same result as in the image below?
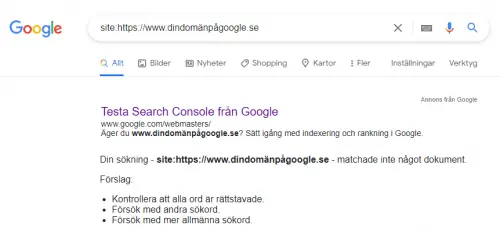
If yes: your site is not indexed.
Okay, so we’ve established that your site isn’t indexed. Now we need to dig deeper and try to find out why. Over the years, we’ve solved many different indexing issues for our clients, and we’ve seen that some problems are more common than others.
If no: Do you instead see links to pages from your site? That means your site is indexed.
Your site is telling search engines not to index it
The most common reason a site isn’t indexed is that it accidentally has a “noindex” tag applied to the entire site. You can see this in the source code. This tag essentially tells all search engines: “I don’t want search engines to index this page.”
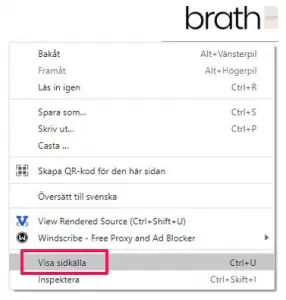
To check if you have a “noindex” tag, right-click in your browser while on your site and choose “View Page Source”:
Then press Ctrl+F to search and look for “noindex” (without quotation marks).
Do you find something that looks like this in your source code?
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”>
Yes, then that page is blocked from being indexed. Try checking a few more pages on your site — if they all show the same thing, it’s time to contact your web support team to get help removing the tag.
2. Your site has ended up in a filter
Google has different methods to filter out websites it considers to be of poor quality or even harmful to its users. When a site ends up in a filter, it becomes more or less de-indexed and removed from Google Search. Your site can be caught in a filter for several reasons:
If your site provides advice in areas like health, finance, or safety that isn’t scientific or doesn’t align with established medical or financial consensus, you may be filtered out so that the site doesn’t risk harming a user’s health, finances, or security.
- If the content on your site, such as text and images, is copied from other places.
- If your site contains spammy links. For example, if you’ve filled your site with links to unsafe sources or sites trying to trick people, it will most likely trigger a filter.
- If your site is almost empty: a site with thin content that doesn’t help or interest users can end up in a filter and be excluded from the search results.
How do you know if your site has ended up in a filter?
Unfortunately, you won’t get a notification from Google telling you that your site has been filtered. It can be a bit tricky to figure out whether your site is in a filter or not. Most site owners who are affected can only guess by carefully examining their own site.
Have you previously ranked on Google and driven traffic, but now all the numbers have dropped to the bottom? Do you recognize your own site in any of the points mentioned above? If so, your site may be caught in a filter.
Getting back from a filter is difficult and takes time. There is no “quick fix” once a site has been filtered. If you suspect your site has ended up in a filter, you’ll likely need professional help to get out of it.
Here you can find more reading about filters and manual actions.
3. Your site is too slow and/or broken’
Everyone who uses the internet wants results quickly — and so does Google. Users won’t wait around for a site that takes several seconds to load. In fact, most people only wait about 3 seconds before they give up, go back to the search results, and click on another link.
Of course, Google wants to deliver relevant and fast websites to its users, which is why site speed has become a factor it looks at when determining where a site should rank in Google Search. You can’t rank high in the search results if your site is slow. And if it’s really slow, Google may choose not to show it at all.
The same goes if your site has many pages that don’t work or contain broken elements. A site with lots of broken pages risks being excluded from the search results entirely.
4. You are blocking search engines in robots.txt
You usually block search engines from sensitive pages such as login pages and the shopping cart. But it’s easy to write the wrong instructions and end up preventing search engines from accessing important pages — or even your entire site.
The robots.txt file contains instructions for search engines, telling them how they are allowed to behave on your site. For example, you can block search engines from visiting certain pages. But if the settings are wrong, you might block them from crawling every page.
Since robots.txt can be tricky to read and understand, it’s always a good idea to get help from someone with technical expertise. We recommend contacting your web support team if you’re experiencing issues with your robots.txt file.
5. Your site is brand new
If you’ve just launched your website, you’ll need a bit of patience. It can take some time before Google discovers and indexes your site. You can speed up the process by creating a Google Search Console account and uploading a sitemap there. Google sees this as a signal to crawl the sitemap, which can help accelerate indexing.
However, if more than two weeks have passed since your site went live, something else might be causing issues. In that case, we recommend revisiting the other reasons mentioned in this article.
As you can see, there are several things to investigate when your site is having indexing problems. Indexing plays a huge role in how and when your page appears, and if none of these points apply, it may be time to contact specialists who can take a deeper look at your site.