One of the fundamental aspects of SEO is indexing. If Google cannot, or chooses not to, store the documents on your site in its index, no other actions matter because there’s nothing to display.
In this blog post, I will discuss the reasons and solutions for both situations: when Google doesn’t index anything on a site and when they fail to index parts of a site. Since this is a general post, the tips here may not resolve your specific problem, but hopefully, they will help you identify where it might make sense to start looking for issues.
Find out if a page is indexed
It’s quite easy to find out if Google has indexed your site. Go to Google and in the search field, type site:domainname.com. This will display all the pages that Google has in its index, and above the results, it will show how many pages are indexed in total.
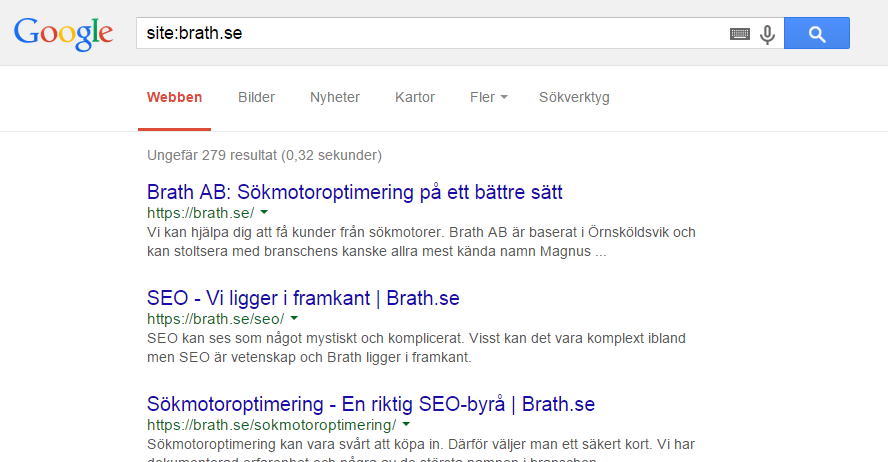
In our case, there are 279 pages indexed, which is a fairly reasonable number considering that the site has around 170 blog posts, about 50 pages of various types, and around 30 tags and categories, some with multiple pages. On a site of our size, most pages should be indexed; if they’re not, something is probably wrong. When sites grow (think large e-commerce sites or news websites), it’s common for not every single page to be indexed. This is not a problem, as long as most pages are.
Such a search also provides an indication of how important Google thinks the pages on your site are, based on the order in which they appear in the results. Normally, the index page should be the one listed first, otherwise, it might indicate that there is an issue with your site.
If you have many pages on your site and want to know if a specific page is indexed, you can search the same way as above, but input the full URL instead:
No pages on the site are indexed
If Google hasn’t managed to index any pages on your site, you probably either have a fairly easy-to-fix issue or a long uphill battle ahead of you.
The most common reason for this is that Google has somehow been blocked from visiting the site. Start by opening the source code of a page (right-click anywhere and select: “View source”, “View page source”, or similar) and look for a “robots” tag that contains “noindex”
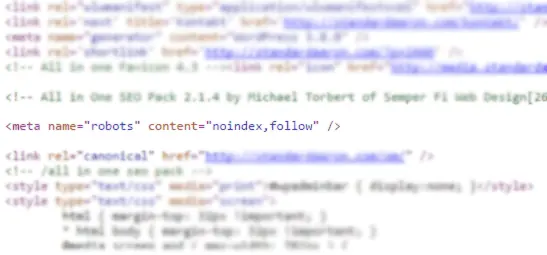
If you find such a tag, it is likely the problem, and you simply need to remove it. Exactly how you do this depends on what CMS you’re using.
If you don’t find that tag, the next step is to check your robots.txt file. You can find it by typing your domain name in the browser’s address bar and adding /robots.txt. Here, you want to look for a line that says: “Disallow: /”. If such a line exists, it means you’re not allowing Google and other bots to visit your site. Remove the “/” and that should solve the problem!
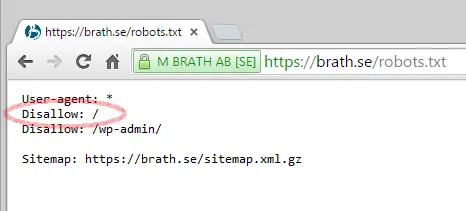
If you don’t find either a noindex tag or the / in the robots.txt, things unfortunately start to get a bit tricky. It’s likely that Google either can’t find your site at all or that they really don’t like it. Make sure you have at least one external link pointing to the site, or add a few so that Google can find it. Go into Google Search Console (formerly Google Webmaster Tools) and check for any messages about a manual action against the site, whether Google is indicating problems reading your documents, and that there is a sitemap uploaded. If none of this helps, the best advice is to contact a professional SEO specialist who can take a look at your site.
Parts of the site are not indexed
Now we get to the difficult part when it comes to finding and solving problems. When a specific part of a site isn’t indexed, or when seemingly random pages aren’t picked up by Google, it can be caused by almost anything. So I thought I’d quickly go over some common reasons why Google might choose not to save certain pages.
- Poor structure
The most common issue is that the structure of the site, the internal links, and menus are poorly built. Either because there are so many links in the menus that Google can’t crawl them all, or important sections are missing from the main menus, and the bot has to rely on backdoors. Make sure you have a clear hierarchical structure for your content. This becomes more important as the site grows.
- Internally duplicated content
Having many pages with the same or very similar content is something Google doesn’t like. This might happen if you have many similar products, for example, or if there’s a technical issue creating page copies, such as by adding parameters or session IDs. The solution is to create unique pages or use canonical tags if it’s a technical issue.
- Externally duplicated content
If much of your content also exists on other sites—because you share a supplier or because your content has been copied—it’s common for Google to choose to only index pages from one site. The solution here is to create content that only exists on your site.
- Thin content
When Google comes across a site with many pages but little valuable information, they might choose to ignore that site. In that case, create more interesting content.
- Too few links
If your site has too few links, Google might sometimes think that your site isn’t interesting enough to crawl all pages. You can solve this by acquiring more relevant links.
- Too many/spammy links
- If you’ve acquired many poor links, Google might view them as a negative signal and decide not to show those pages. Fix this by removing bad links or, in the worst case, using the Disavow Tool.
- Too much advertising
- If Google encounters a site with too much advertising, especially if it’s “above the fold,” they may sometimes remove those pages from their index. Make sure your own unique content takes up the most space on the page, not the ads.
There are more reasons for indexing issues, but these are the ones I encounter most often. To summarize the text and give general advice: Build a site with interesting content and a good structure. That solves most difficulties with Google.
